Products

Anti-Mosquito
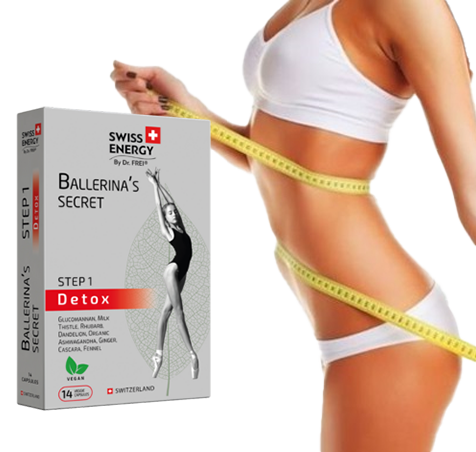

BALLERINA’S SECRET

Beauty Line

Black Garlic

Black Seed Oil
Bones & Joints

Collagen
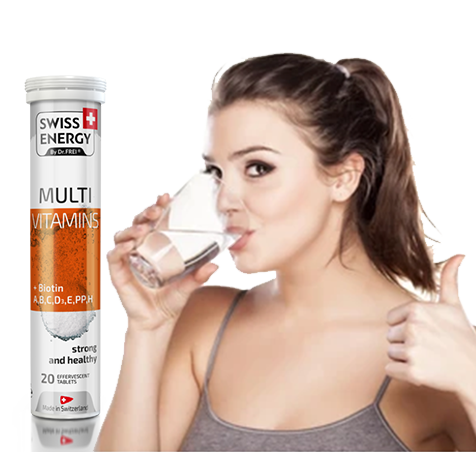

Effervescent Tablets
Energy & Functional Drinks
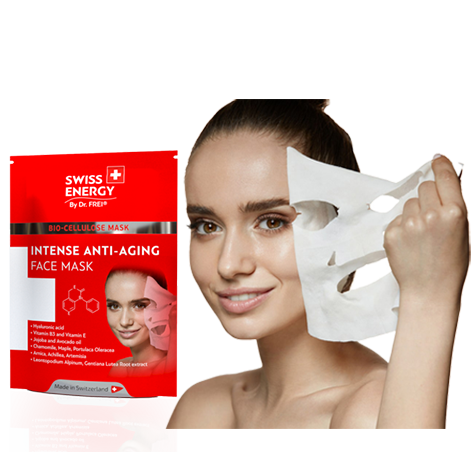

Face Mask

Foot Spray

Functional Chewing Gum

Guten Morgen

Hair Care
Healthy Pregnancy
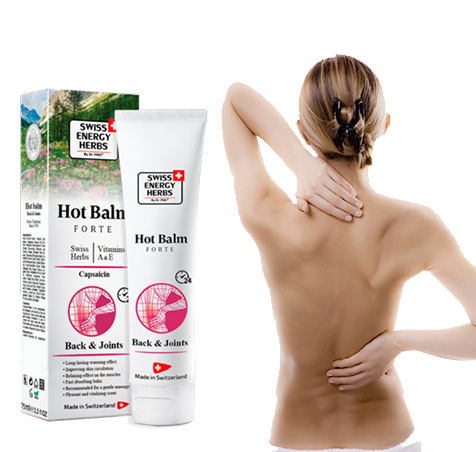

Herbal Balms
Herbal Lozenges
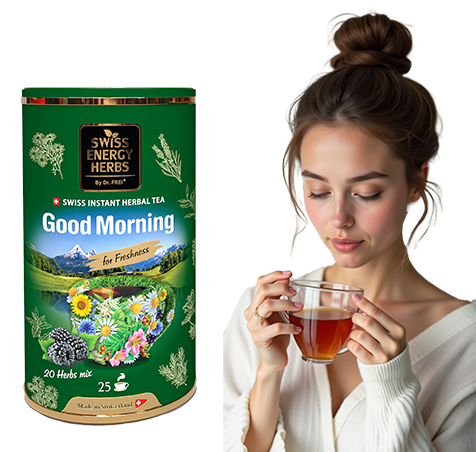

Herbal Tea
Liver Support

Omega
Probiotics

Resveratrol

Sexual Health

Sports & Fit

Sustained Release Capsules

Vitamin Cosmetics

Vitamin Elixirs

Vitamins for Children

Vitamins Lollipops

WHITE TOMATO

SWISS ENERGY food supplements have been specially developed by SWISS ENERGY PHARMA GmbH, Switzerland, taking into account recommendations of the leading health care specialists.
In an effort for a daily, optimal health care Swiss Energy Pharma GmbH uses high quality ingredients in the manufacturing of Swiss Energy vitamins. Swiss Energy vitamins are important components of an active life. They compensate the lack of nutrition, being useful for prevention of diseases, and are necessary taking sports.